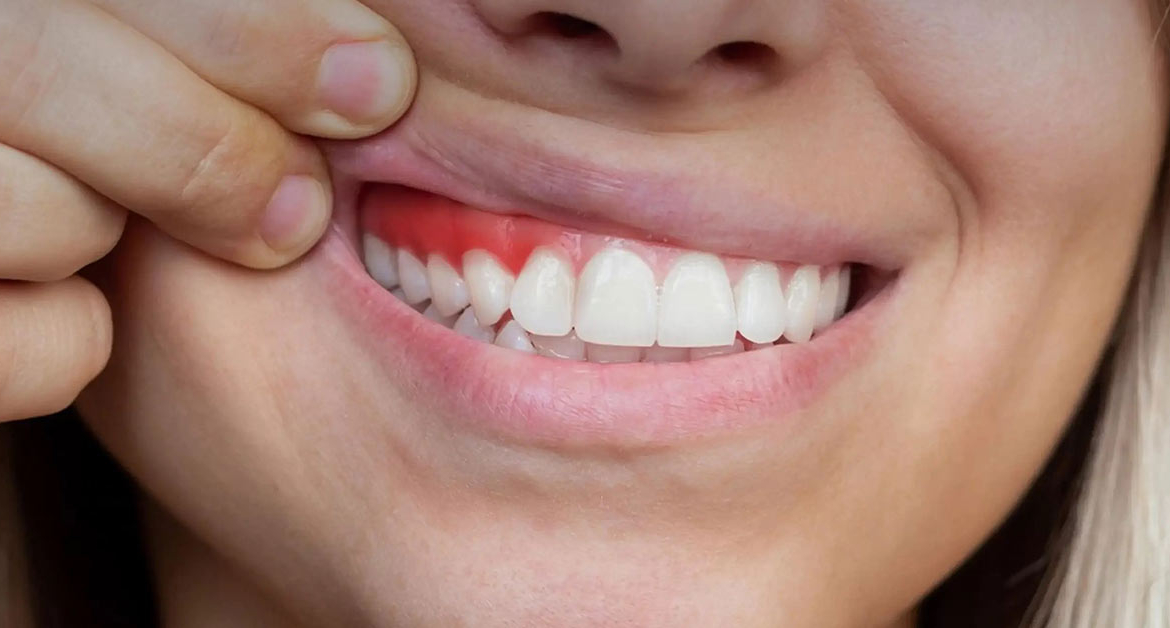
The gingival withdrawal is the condition of releasing the root of the tooth by withdrawing the gum around the teeth. This occurs with damage to the gum and usually occurs as a result of not paying attention to oral hygiene. There may be several reasons for gum withdrawal; These include bad oral hygiene, smoking, excessive pressure during toothbrush, and periodontal diseases.
Symptoms of gingival withdrawal include the longer the teeth appear, sensitivity and pain sensation, and stains on the root surface become visible. If you are experiencing these symptoms or worried, it is important to consult a periodontist (gingival diseases specialist) or a dentist.
On the other hand, you can prevent this situation by paying attention to a good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly. It is also important to avoid smoking.
Causes gum withdrawal?
Gingival recession can be for several different reasons. These include bad oral hygiene, smoking, excessive pressure during toothbrush, and periodontal diseases.
Bad Oral Hygiene: When the teeth are not brushed regularly and the dental floss is not used, the plaque accumulates and may cause it to be pulled by irritating the gum.
Smoking: Smoking can prevent the renewal of the gums in a healthy way by reducing blood circulation. This may cause gingival withdrawal.
Brushing teeth with excessive pressure: Brushing teeth very hard or incorrectly can cause them to withdraw by irritating the tissues that support the female and female.
Periodontal Diseases: Periodontal diseases, ie infections caused by bacteria are another common cause. When this disease progresses, it can cause bone loss and consequently gum withdrawal.
In addition to these reasons, genetic factors may also play a role. In addition, hormonal changes, aging process and some medical conditions can contribute to this problem.